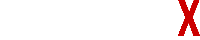By Benoit de Bénazé, Director at JCRA
We have seen a surge in European public-to-private (P2P) transactions, with takeovers of listed companies accounting for 21% of total deal value compared to 16% over the same period last year. The UK market has been particularly active, with the £4.8bn take-private of Merlin Entertainments being a particularly notable case.
A significant driver of this activity has been foreign buyers (e.g. funds denominated in EUR or USD) spotting opportunistic FX entry points, with both GBP and EUR trading at historic lows. Just as important are the different dynamics that drive valuation multiples for private and public companies, and the potential arbitrage opportunities these can give rise to. An excellent discussion of this is given in Bain & Co’s “Global Private Equity Report 2019”.
In the UK, bids for listed companies are governed by the City Code on Takeovers and Mergers. Those who have contemplated UK P2P transactions in the past will be well aware of the “certain funds” requirement, which specifies that the bidder must have definitive (i.e. unconditional) funding in place by the time the offer is announced. While the bidder’s financial advisor is obliged to confirm this in the offer document, this confirmation is not an absolute guarantee. Indeed, there are precedents for the advisor themselves being call on to provide funds where the bidder’s funding sources have fallen through.
In the context of cross-border acquisitions, appropriate management of the associated FX risk is critical for ensuring that the certain funds requirement is met. Unless the non-sterling funds have enough headroom to cover the most extreme FX fluctuations between announcement and closing, this means hedging arrangements must be put in place before announcement. In the current environment of geopolitical uncertainty leading to significant FX volatility, it is rare to see a serious investor remaining unhedged.
As a result, deal-contingent (“DC”) hedging continues to grow in popularity alongside more traditional instruments (forwards, options etc.). DC hedging instruments have the significant advantage that they fall away without settlement or cost in the event that the associated acquisition fails to complete. As such, they are increasingly the solution of choice for cross-border M&A participants looking to lock in their FX rate ahead of completion.
Of course, this protection comes at a price. In the case of a DC forward, a premium will be embedded into the forward rate to compensate the hedge provider for the M&A risk. That said, this premium is typically a fraction of that which would be paid for the equivalent FX option. As such, DC forwards combine the best characteristics of an option and a forward, often at an extremely attractive price.
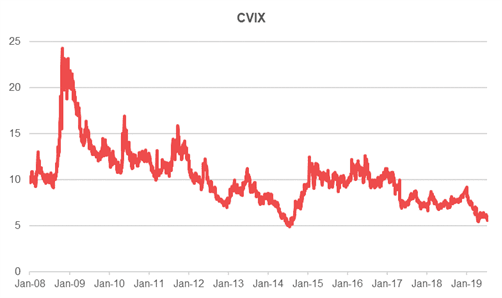
With interloper risk and deal failure being far from theoretical risks (think of Bain and Apollo losing out of the acquisition of RPC earlier this year), the success of DC solutions is perhaps not surprising. It is also interesting to note that, despite the geopolitical uncertainty, the pricing of any currency volatility based product is relatively attractive. The CVIX Index, which measures three-month implied volatility weighted across several major currency pairs, is currently trading at historically low levels.
As with all other aspects of the transaction, good preparation is critical the financial market risks associated with a P2P deal.
Here are our top tips:
- Carry out an extensive analysis of the different financial risks (FX, IR, others), including the timing of these risks (announcement, debt allocation, closing/post-closing)
- Understand the closing/completion risks of the different hedging strategies (vanilla and deal contingent)
- Carefully select the banks to involve in the hedging process. It is common to use banks involved in either the M&A and/or the financing to assist with the hedging. All major commercial banks will offer FX forwards options on G10 currencies, but not all are able to offer DC hedging. So using banks in the transaction is not a guarantee that the desired hedging instrument will be available at competitive pricing. In addition, more and more deals involve M&A boutiques and debt funds with no hedging capabilities, so the bidder may well need to involve external counterparties. For P2P transactions in the UK, there are restrictions on the number of external counterparties that can be involved
- Don’t leave it to the last minute. It could take up to two weeks to arrange for a hedging strategy, Waiting until the announcement is looming is likely to result in suboptimal hedging at a non-competitive pricing or, worse, a delay in announcement
It is common to use a hedging advisor to coordinate these work streams at a time when resources are limited timing is critical. JCRA has many years of experience helping Corporates and Private Equity funds to implement such solutions, including management of deal structure, due diligence coordination for DC hedging, pricing transparency, negotiation of documentation negotiation, accounting support and execution.
Tradersdna is a leading digital and social media platform for traders and investors. Tradersdna offers premiere resources for trading and investing education, digital resources for personal finance, market analysis and free trading guides. More about TradersDNA Features: What Does It Take to Become an Aggressive Trader? | Everything You Need to Know About White Label Trading Software | Advantages of Automated Forex Trading